Overactive bladder syndrome (AAMS) is a syndrome in which a sudden and irreversible urge to urinate is seen as the main complaint. The physical functions, social lives and emotional states of patients with overactive bladder syndrome are negatively affected.
AAMS can occur due to many neurological and non-neurological reasons. Any event that causes disruption in the functioning of the musculoskeletal and neurological system can disrupt normal bladder control and cause urge urinary incontinence.
Overactive bladder syndrome seriously impacts quality of life. Especially urge urinary incontinence is one of the important reasons why elderly patients are sent to nursing homes.
Overactive bladder syndrome may also have an economic impact due to the increased risk of skin infections, urinary tract infections, falls and fractures in elderly patients. If the patient has complaints, diagnosis can be made with a few simple tests.
Treatment options include bladder training, medications, bladder botox and surgery.
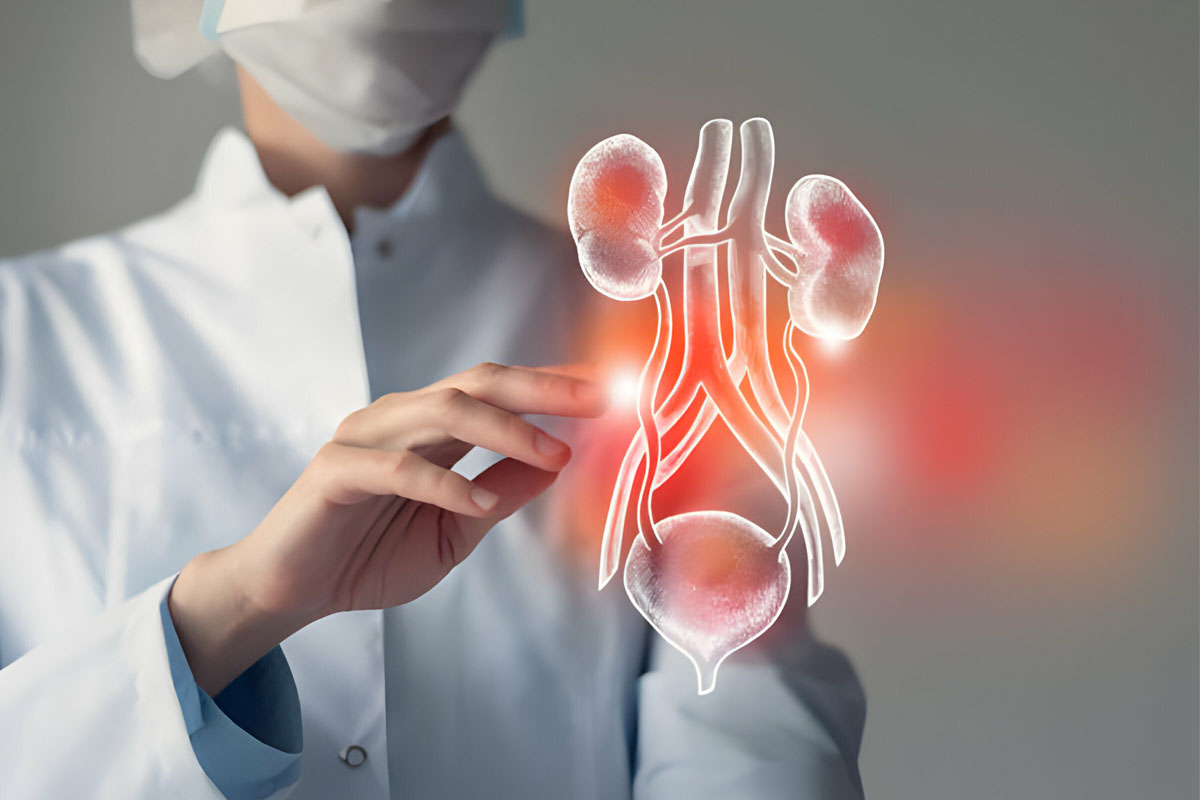
What is Bladder? What is it for?
The bladder, that is, the urinary bladder, is an organ consisting of balloon-shaped muscle tissue in which urine from the kidneys accumulates. It is located in the lower part of the abdomen, on the bone region called the pelvis, attached to other organs and the pelvic bone by ligaments. When the amount of urine in the bladder reaches a certain amount, the urine in the bladder is expelled through the external urinary tract (urethra) through urination.
While the urinary bladder takes a round shape when it is completely filled, it becomes smaller after urination. The normal bladder has the capacity to accumulate 300-500 ml of urine.